임상식물병리학연구실
ANU CLINICAL PLANT PATHOLOGY LAB (APPL)
- 지도교수 : 전용호
- 실험실원 : 김중연, 김희진, 권성문, 김승환, 강동훈, 박현진, 허윤정, 김다영, 장로사, 권혁태, 발라라주 박사, 이연미 박사
- 전화번호 : 7119(실험실, 식물종합병원)
Research
We pursue translational research that brings problems occurring in the field to the laboratory and solves them. We apply the researched solution to the field. We study the diagnosis and mechanism of plant diseases and the development of microbial agents for environmentally-friendly control.
1. Diagnosis of Plant Diseases
The diagnosis of plant problems is the first step in an effective and economic management program. Early detection and accurate diagnosis of plant diseases is the cornerstone of effective, cost-efficient plant disease management. Whether detecting new, emerging, or endemic plant diseases, plant diagnostic laboratories serve public and private interests and encourage integrated management of plant problems. My program is focused around the development and validation of diagnostic technologies, utilization of relevant diagnostic methods to accurately diagnose plant problems in the plant disease clinic, and practical training of students and professionals in plant problem diagnosis. Each diagnosis with disease management strategies that are research-based, economically sound, and environmentally appropriate for the situation.
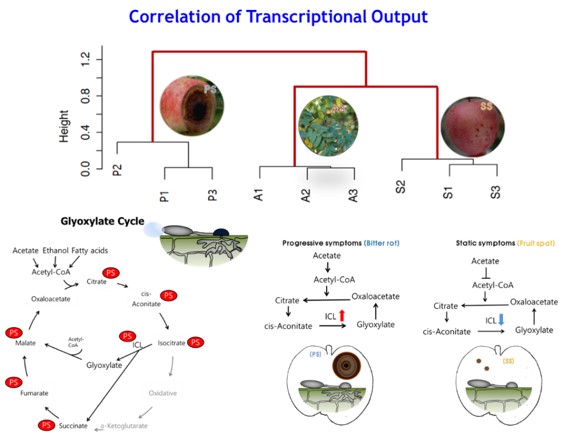
2. Apple Bitter Rot Research
Apple Bitter Rot Season is Upon Us. While fruit rots have a variety of causes, the most common fungal fruit rot of apple in Korea is bitter rot. The disease results in rotten, inedible fruit. Fungicides are available for management; however, sanitation is critical for disease prevention. Ongoing research at the Clinical Plant Pathology Lab is providing new insights and understanding of the pathogens that cause bitter rot.
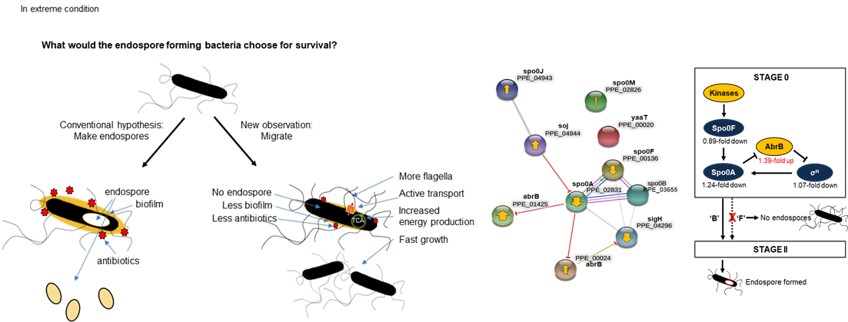
3. Phenotypic Variation of Useful Bacteria
Paenibacillus polymyxa has been frequently used as a biological control agent (BCA) globally due to its rhizosphere competence and tolerance to harsh environmental conditions. Some other Paenibacillus spp., have been shown to display phenotypic variation, including reversible switching between the rod- and coccoid-shaped cells. A recent study showed that P. polymyxa also formed distinctly shaped colonies when cultured on a solid medium presumably without involving any genetic alterations. Such microbial phenotypic variation appears to be part of survival strategies under varying environmental conditions. The objective of this study was to determine the molecular basis of phenotypic variation through a comparative analysis of B- and F-type cells and to help develop ways to prevent or minimize phenotype variation during mass production.
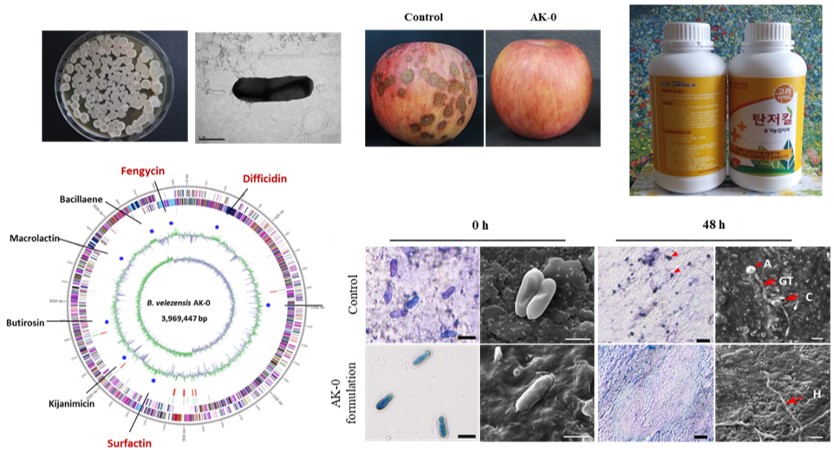
4. Discovery of novel biofungicide
Biological control by PGPR has emerged as an alternative to reduce the use of conventional agricultural inputs for improving the quantity and quality of the crop produce. In recent years, the yield and quality of many fruit crops have been reduced by attacking various diseases caused by phytopathogens; this can be overcome using biological control agents (BCAs). Bacillus velezensis, an antagonistic bacterium produces several antimicrobial compounds as secondary metabolites against various phytopathogens. The Bacillus sp. produces spores, which can be used for the development of an effective microbial biopesticide formulation in the form of a BCA. To gain an in-depth understanding of the biocontrol ability of AK-0 against apple bitter rot, this study reports the complete genome sequence of AK-0. To further identify the divergent genomic characteristic among other Bacillus strains, a comparative genome analysis was performed.
Recent SCI Publications
Kim YS, Lee YM, Cheon WS, Park JW, Kwon HT, Balaraju K, Yoon YJ, Jeon YH. 2021. Characterization of Bacillus velezensis AK-0 as a biocontrol agent against apple bitter rot caused by Colletotrichum gloeosporioides. Scientific Reports.
Lee YM, Lee YY, Kim YS, Mok YS, Yoo SJ, Jeon YH. 2021. Effect of cold plasma treatment on the enhancement of seed germination and sterilization of ginseng seeds, and disease suppression of root rot of ginseng. J. Ginseng Res.
Lee YM, Kim YS, Balaraju K, Seo YS, Park JW, Ryu CM, Park SH, Kim JF, Kang SC, Jeon YH. 2020. Molecular changes associated with spontaneous phenotypic variation of Paenibacillus polymyxa, a commonly used biocontrol agent, and temperature-dependent control of variation. Scientific Reports.
Lee YY, Lee YM, Kim YS, Kim HS, Jeon YH. 2020. Control of Red Pepper Anthracnose Using Bacillus subtilis YGB36, a Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacterium. Res. Plant Dis. 26, 8-18.
Lim YJ, Ryu DK, Kang MK, Jeon YH, Park DH. 2019. Draft genome sequences of Pseudomonas syringae pv. syringae strain WSPS007 causing bacterial shoot blight on apple. Kor. J. Microbiol. 55, 80-82.
Lee Y, Choi O, Kang B, Kim SH, Kim JW, Choi JH, Lee JW, Nam JH, Park HJ, Choi YJ, Kim DW, Park YS, Choi YJ, Lee JS, Kim B, Lee DJ, Park SY, Kim GH, Kim YM, Jung SY, Lee Y, Jeon YH, Kim YS, Kwon HT, Kim JY, Shin YH, Jeun YC. 2019. Monitoring Reports about Nine High Risk Plant Pathogens in South Korea. J Agri. Life Sci. 54, 17-23.
Kim YS, Kwon HT, Hong SB, Jeon YH. 2019. Occurrence of Bunch Rot Disease Caused by Aspergillus tubingensis on Shine Muscat Grape. Res. Plant Dis. 25, 220-225.
Kim YS, Yun YJ, Jeon YH. 2018. First Report of Black Rot Caused by Diplodia seriata on Apple. Res. Plant Dis. 24, 321-327.
Jung WK, Kim YS, Choi JK, Kim SH, Jang MH, Kwon TL, Jeon YH. First Report of Bacterial Root Rot Caused by Serratia plymuthica on Panax ginseng. Res. Plant Dis. 24, 332-338.
Kim YS, Balaraju K, Jeon YH. 2017. Biological characteristics of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens AK-0 and suppression of ginseng root rot caused by Cylindrocarpon destructans. J. Appl. Microbiol. 122, 166-179.
Park, GH, Song, HM, Kim YS, Jeon YH, Koo JS, Jeong HJ, Jeong JB, 2017. Anti-cancer activity of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens AK-0 through cyclin D1 proteasomal degradation via GSK3β-dependent phosphorylation of threonine-286. Pharmazie 72, 348-354.
Kim YS, Balaraju K, Jeon YH. 2016. Effects of rhizobacteria Paenibacillus polymyxa APEC136 and Bacillus subtilis APEC170 on the suppression of postharvest pathogens of apple fruits. J. Zhejiang Univ. SCIENCE B. 17, 931-940.
Cheon W, Kim YS, Balaraju K, Kim BS, Lee BH, Jeon YH. 2016. Postharvest disease control of Colletotrichum gloeosporioides and Penicillium expansum on stored apples by gamma irradiation combined with fumigation. Plant Pathol. J. 32, 460-468.
Kim YS, Balaraju K, Jeon YH. 2016. Biological control of apple anthracnose by Paenibacillus polymyxa APEC128, an antagonistic rhizobacterium. Plant Pathol. J. 32(3): 254-259.
Cheon W, Jeon YH. 2016. Anthracnose caused by Colletotrichum acutatum in Robinia pseudoacasia. Res. Plant Dis. 22, 127-131.
Chang SP, Jeon YH, Kim YH. 2016. Defense-related responses in fruit of the nonhost chili pepper against Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. glycines infection. Plant Pathol. J. 32, 1-10.
Kim YS, Balaraju K, Kim YH, Jeon YH. 2016. Biological characteristics of Paenibacillus polymyxa GBR-1 involved in root rot of stored Korean ginseng. J. Ginseng Res. 40, 453-461.
Cheon W, Kim YS, Balaraju K, Kim BS, Lee BH, Jeon YH. 2016. Postharvest control of Botrytis cinerea and Monilinia fructigena in apples by gamma irradiation combined with fumigation. J. Food Prot. 79, 1410-1417.
Cheon W, Jeon YH. 2016. First Report of Anthracnose Caused by Colletotrichum spaethianum on Fragrant Plantain Lily in Korea. Plant Dis. 100, 1498.
Kim YS, Jeon YH. 2016. First Report of Orostachys malacophyllus Soft Rot Caused by Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. carotovorumin Korea. Plant Dis. 100, 208.
Cheon W, Lee SG, Jeon YH. 2016. First Report on Fruit Spot Caused by Colletotrichum gloeosporioides in Apple (Malus pumila Mill.) in Korea. Plant Dis. 100, 210.